What is an Eye Refraction Examination?
by Admin
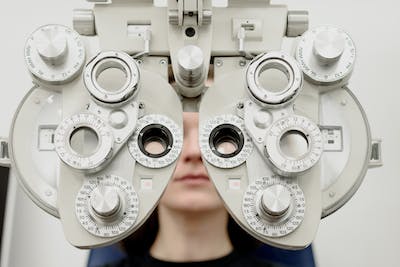
Refractions are an important component of a complete eye exam. They help doctors establish prescriptions and detect diseases that do not show symptoms until much later.
The first step in the refraction is to measure how light bends through your pupil as well as the lens on each eye. They can then identify refractive issues such as nearsightedness and farsightedness.
What is an refractions test?
Refractions are an essential part in eye exams. They provide your optometrist/ophthalmologist the information necessary to determine what prescription you will need for either glasses or contact lenses. Also called vision tests.
Your doctor will assess your refractive problem using equipment that resembles a large, mask-like mask with eye holes. They will shine different lights into your eyes and then ask to read an optical chart at a 20-foot standard distance. They may also ask to see if the letters are clearer than expected.
Refraction measurements measure how light enters into and strikes the retina of your eyeball at the back, and how effectively the cornea and lenses focus the light on retina. This test will inform your optometrist and Ophthalmologist which lens prescription allows for 20/20.
How do you conduct a test for refraction?
Refractions are performed during an eye exam. They should be done at least once every two to three years in order to detect any health conditions. They can also be used to determine how much vision correction is needed. According NerdWallet, most people should get one every two or three years.
Refraction testing doesn't usually cause discomfort and isn’t too expensive. During it, your doctor will have you look through a device called an eyewear called a “phoropter” that resembles a lensed mask to view a graph with letters that shrink from top to bottom. Your eyesight specialist will adjust your lenses until the letters are clear. This allows them to accurately estimate how much lens power you need for contacts or glasses.
What are the results of a refractive test?
Refraction tests can provide your doctor with results for a prescription of eyeglasses, contact lenses or other eye care products. They may also be able to detect eye diseases or conditions that are present but not yet manifested.
Refraction is done by using a device, called a "phoropter", with lenses that have different strengths. You will first be instructed to look at a wall chart and read a number of symbols or letters through each lens. Your eye doctor will then ask you which lens provides better clarity.
Medicare and some other medical plans will not cover refractions. CMS (Centers for Medicare Medicaid Services), the federal agency that oversees Medicare and other medical plans, has determined that refractions are not essential for maintaining eye health.
What are risks associated with a failure to conduct a refraction examination?
Refractor Tests Every One or Two Years Help Eye Doctors Track Vision Changes That Occur Regularly and Determine the Needed Prescription for Each Patient.
Eye doctors use a device called a “phoropter” to perform refraction during an eye exam. This large machine has many dials, switches and dials. Patients look through the lenses to see how clear they can see before their doctor writes a prescription.
Diabetes patients should have annual refractions to detect diabetic and glaucoma. They are both related to an accumulation of pressure inside the eye. Eye doctors can detect these issues early and help save the patients' vision.
https://www.nuvisioncenters.com/excel/
Refractions are an important component of a complete eye exam. They help doctors establish prescriptions and detect diseases that do not show symptoms until much later. The first step in the refraction is to measure how light bends through your pupil as well as the lens on each eye. They can then identify refractive issues…
Recent Posts
- Anew Vision: Leading the Way in Sober Living and Transitional Independent Living Programs in Fort Worth, TX
- JCTZ Garage Doors Revolutionizes Garage Door Services in Sun City, Surprise, and Buckeye, AZ
- Southwest Patio: Revolutionizing Outdoor Living with Expert Gazebo Installations and Four Seasons Patio Covers
- Why Partnering with a Local Marketing Agency is Essential for Website Development Success
- Expert Lawn Care Lubbock Advocates for Property Care: Combatting Weed Growth and Preserving Curb Appeal
